How Does a Soil Moisture Sensors Work?
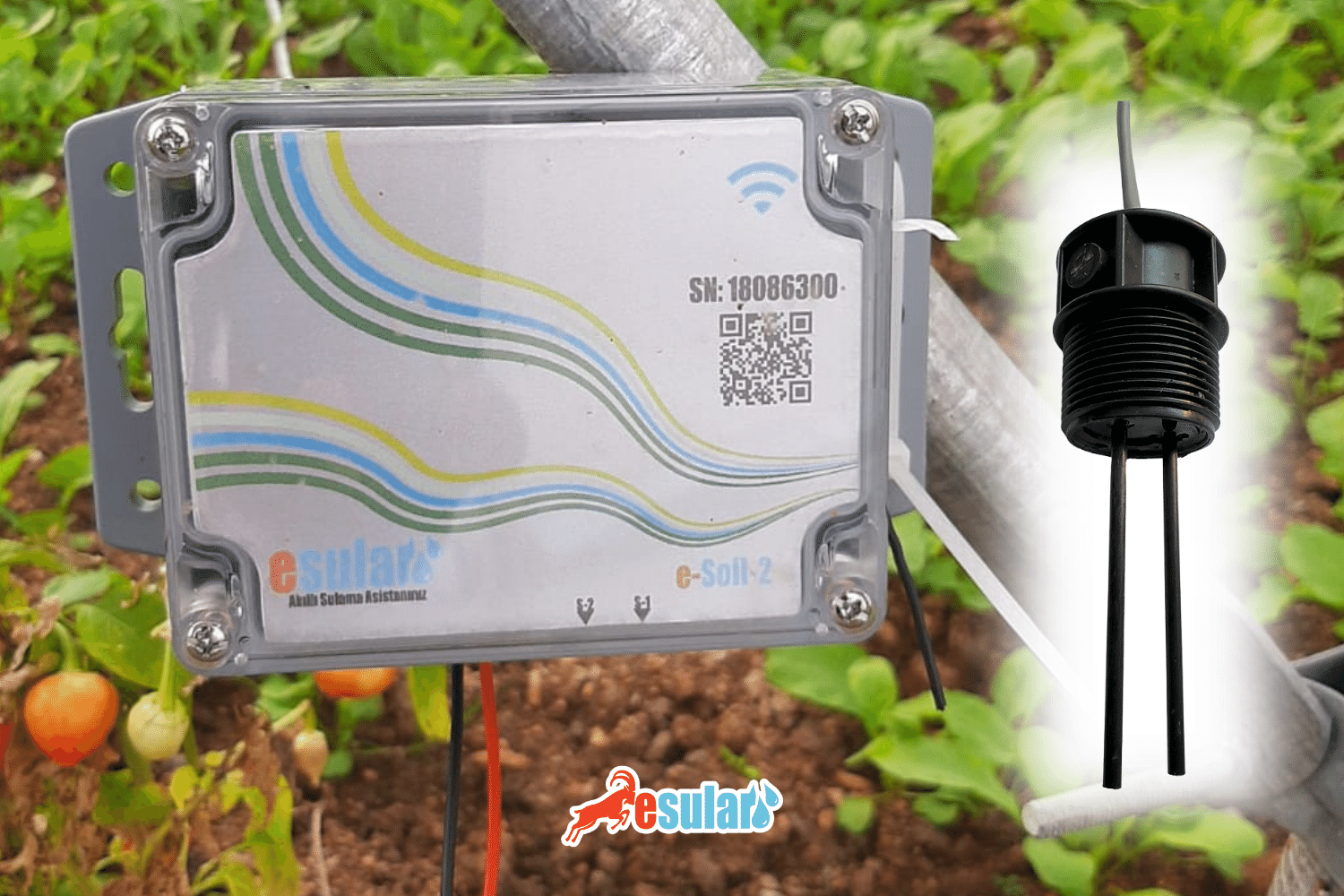
What is the Soil Moisture Sensor?
Soil moisture sensors are devices used in the measurement and monitoring of moisture levels in the soil. These sensors meticulously measure and continuously monitor the moisture levels within the soil, allowing for irrigation to be conducted based on the specific water needs of plants. When the soil becomes dry, they automatically activate the irrigation system, minimizing water consumption and promoting water conservation. Maintaining appropriate moisture levels improves plant health, supports root health, and enhances overall productivity. Soil moisture sensors record and analyze the measured data, contributing to the optimization of irrigation programs. Consequently, they enable more efficient use of water resources in plant cultivation processes, leading to increased agricultural productivity.
What are the Benefits of Soil Moisture Sensor?
Soil moisture sensors have become a crucial tool in increasing agricultural productivity. Some benefits of these sensors include:
- Optimizing Water Usage: Soil moisture sensors optimize irrigation processes by determining the amount of water plants require, ensuring efficient water utilization.
- Improving Plant Health: Proper irrigation reduces plant stress, supports optimal moisture levels, and fosters healthy plant growth.
- Increasing Efficiency: By aiding plants in growing under optimal conditions, soil moisture sensors contribute to enhancing crop yield.
- Time Savings: When integrated with automatic irrigation systems, soil moisture sensors continuously monitor soil conditions and manage irrigation processes automatically, saving time for farmers.
- Data Collection and Analysis: The data obtained allows farmers to analyze past information, aiding in the development of future irrigation strategies.
- Reducing Environmental Impact: Unnecessary irrigation can lead to soil erosion and water waste. Soil moisture sensors reduce environmental impacts by ensuring that only the necessary amount of water is provided.
These sensors play a vital role in sustainable agriculture by promoting efficient water usage, improving crop health, and minimizing environmental effects.

How Does a Soil Moisture Sensor Work?
The Wireless Battery-Powered Soil Moisture Sensor operates with a 3.6V lithium-ion battery. There is no need for any external power or wiring for the sensor to function. With its low power consumption and sleep modes, the sensor has an extended battery life. The sensor interacts with the soil through a probe system buried and in contact with the soil. Values measured at specific intervals through the probes are transmitted to the server. This enables the tracking of soil moisture levels and the planning of necessary irrigation or fertilization processes. These sensors typically include the following main components:
Soil Moisture Sensor: This sensor is used to measure the moisture level in the soil. It detects the moisture level through probes placed in the soil, utilizing electrical conductivity to determine the moisture level.
Microcontroller or Data Processing Unit: A microcontroller or a similar data processing unit processes and analyzes the collected data. This unit receives, processes, and prepares data from the soil moisture sensor for wireless communication.
Wireless Communication Module: This module uses a communication protocol to wirelessly transmit the data collected from the sensor. Protocols such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRa, are commonly used. This enables the moisture level data to be transmitted to a remote receiver or a data collection center.
Battery or Power Source: A power source is required for the sensor to operate. In these devices, a lithium battery is commonly used as the power source. The battery life determines the continuous operability of the sensor.
How to Use Soil Moisture Sensor in Grass Fields
Placing soil moisture sensors in the correct position on turf fields is crucial to enhance irrigation efficiency and ensure that plants are adequately watered. Placement is typically done by paying attention to the following points:
- The sensor should be placed as close as possible to the root zone of the turf. Proximity to the root zone enables more precise measurement of soil moisture levels.
- Probes connected to the sensor should be positioned in a homogeneous area of the turf field. Placing probes in areas with different soil types or water retention characteristics may result in non-uniform data.
- Sensors should be placed in close proximity to the irrigation system. This facilitates the integration of sensors into the irrigation system and makes it easier to control the irrigation system based on soil moisture.
- It is important to place the probes at the correct depth. They are typically positioned at a level appropriate for the depth of the soil in the root zone (for example, at a depth of 15 to 20 cm).

How to Use Soil Moisture Sensor in Orchards?
When placing soil moisture sensors in orchards, selecting the correct position is crucial. In this regard, areas where tree roots are widespread can be suitable for sensor placement. If the trees in your orchard are densely planted, ensure that sensors are evenly distributed. It is important that the areas where sensors are placed are evenly spread across each tree to accurately determine the irrigation needs of each tree. If your orchard is large, using multiple sensors may be more effective. Utilizing sensors with two or three probes at different depths can help better understand soil moisture at various levels, enabling a more precise determination of the irrigation needs of the trees.
Soil Moisture Sensor Application Areas
- Automatic irrigation
- Automatic garden irrigation
- Garden irrigation
- Landscaped areas
- Remote irrigation automation
- Smart irrigation
- Greenhouse automation
- Drip irrigation automation
- Pump control
- Lawn irrigation
- Rooting automation
- Sodding automation
